There are different levels of T-1. Although a T-1 has a maximum of 1.544 Mbit/s, a fractional T-1 might be offered which only uses an integer multiple of 128 kbit/s for bandwidth. In this manner, a customer might only purchase 1/12 or 1/3 of a T-1, which would be 128 kbit/s and 512 kbit/s, respectively.

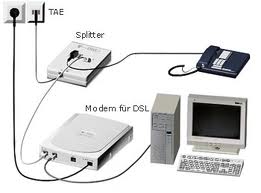 DSL (Digital Subscriber Line):
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line): 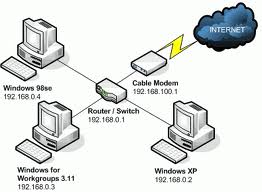 Cable:
Cable: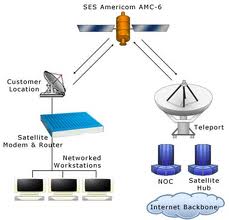 Satellite:
Satellite:
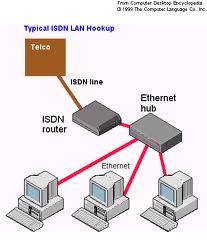 ISDN (Integrated Services Digital
Network):
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital
Network):  T-1:
T-1: 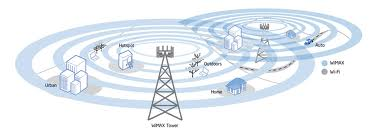 WiMAX:
WiMAX: WiFi
(Wireless Fidelity):
WiFi
(Wireless Fidelity):